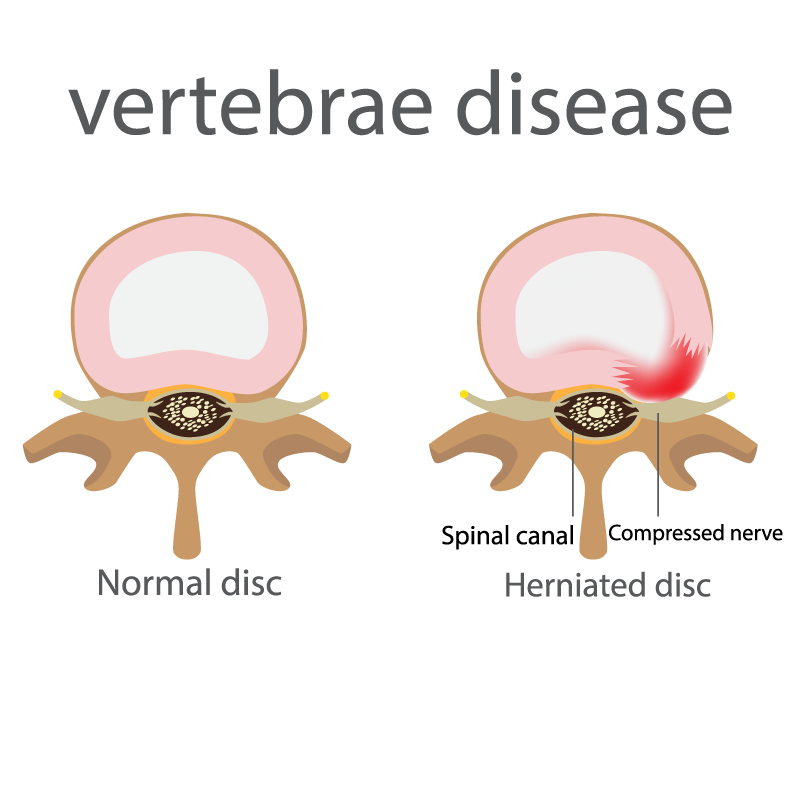
Lumbar Disc Herniation
What is it?
The lumbar disc herniation is a very common spine disorder that causes pain in the lower body as are the lower back and legs. It occurs when the gel like inside of a lumbar intervertebral disc (nucleus pulposus) presses against a nearby nerve. It is mostly common to people that are over their 40’s.
What causes cervical disc herniation?
With aging, the discs become dehydrated and lose their flexibility as well as their ability to absorb the shock from the movements of our body. The outside layer of the disc (annulus fibrosus) forms cracks which allow the inside of the disc to rupture through and irritate the spinal nerves causing pain. There are many variables to what causes a cervical intervertebral disc to herniate. Genetics and age are some of them but very important risk factors are our daily routine and habits. Poor standing, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, lifting weights and strenuous physical activity in older patients can contribute to a disc herniation.
What are the symptoms?
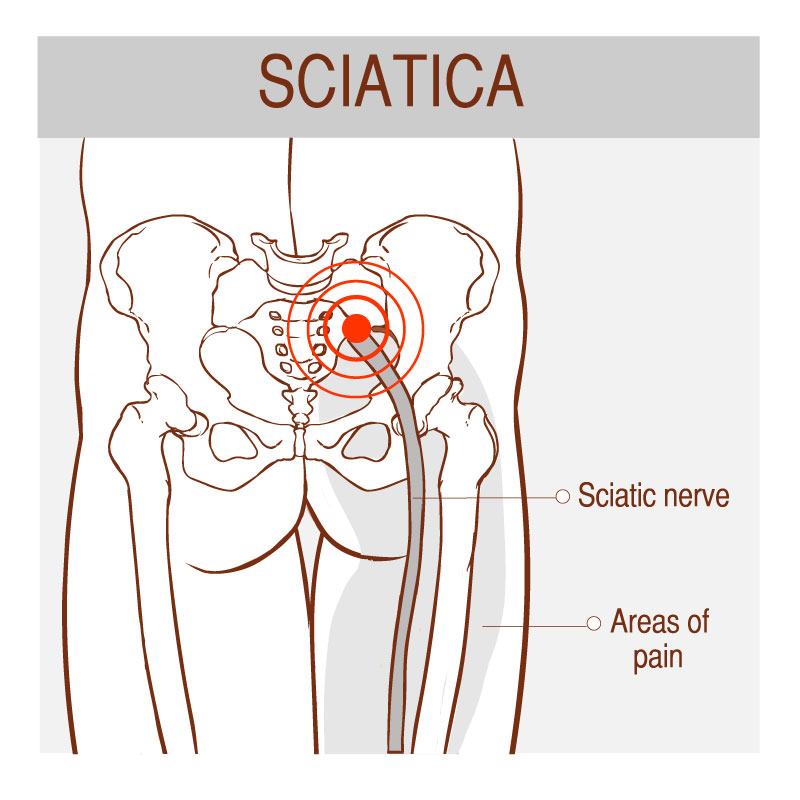
The symptoms may vary depending on the position of the herniated disc, by which nerve is irritated as well as the degree of the herniation. They can occur spontaneously usually after lifting weight or making a sudden move. The pain may radiate from the lower back to the leg and even the toes and it may come and go periodically.
Some of the symptoms affiliated with a cervical herniated disc are:
- Numb or sharp pain in the lower back or leg
- Numbness and tingling sensation in your leg
- Muscle weakness or spasms in the leg or foot
- Bladder control
- Sexual dysfunction
Diagnostic methods
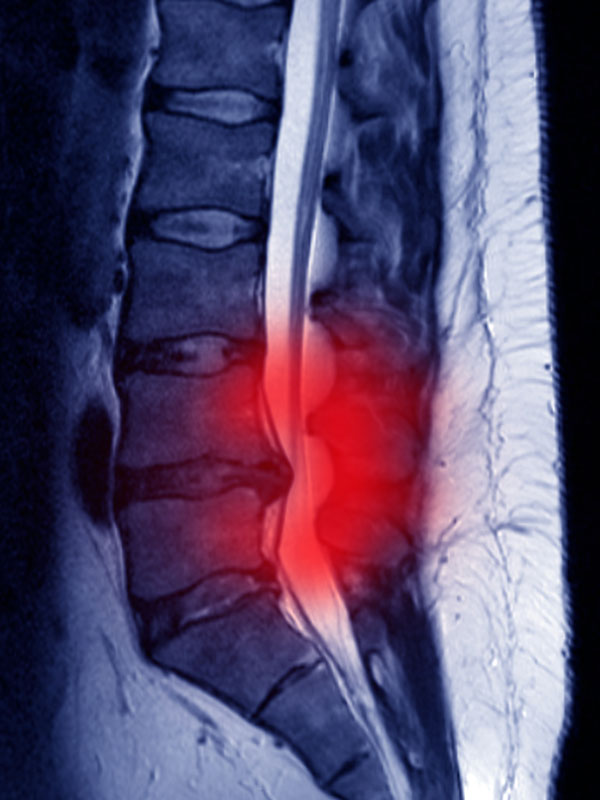
The diagnosis comes from a detailed medical history and a physical and neurological examination from your doctor. The patterns of the pain and your habits can help your doctor estimate your condition. Further examing usually includes an MRI or CT scan.
Treatment Options
The treatment of a cervical herniated disc may not require surgery. Some more conservative methods like rest, medication, an orthopedic cage or physical therapy may help to relieve from the symptoms. If the symptoms do not improve with time or when there is nerve damage, surgery is considered.